- Posted By Dr. Anuranjan Bist
- Comments 0
Table of Contents
Introduction to Neurofeedback
Neurofeedback is an innovative, non-invasive treatment method that harnesses the brain’s natural ability to learn and change. Think of it as a mirror for your brain; it reflects your brain activity back to you in real-time, enabling your brain to make adjustments for better mental health.
Understanding Brainwaves
Our brains constantly generate electrical activity known as brainwaves. These brain waves occur at different frequencies (speeds), measured in Hertz (Hz), and each frequency band corresponds to different states of mind:
- Delta (0.5 – 4 Hz): These are the slowest waves, dominant during deep sleep. They are vital for regeneration and healing.
- Theta (4 – 8 Hz): Common during meditation, dreaming, and creativity. Theta waves can indicate deep relaxation or the initial stages of sleep.
- Alpha (8 – 13 Hz): Prominent during relaxed but alert states, like daydreaming or gentle meditation.
- Beta (13 – 30 Hz): Active during waking consciousness, logical thinking, and problem-solving.
- Gamma (30 – 100 Hz): The fastest waves, involved in high-level information processing, learning, and memory.
Measuring Brainwave Patterns
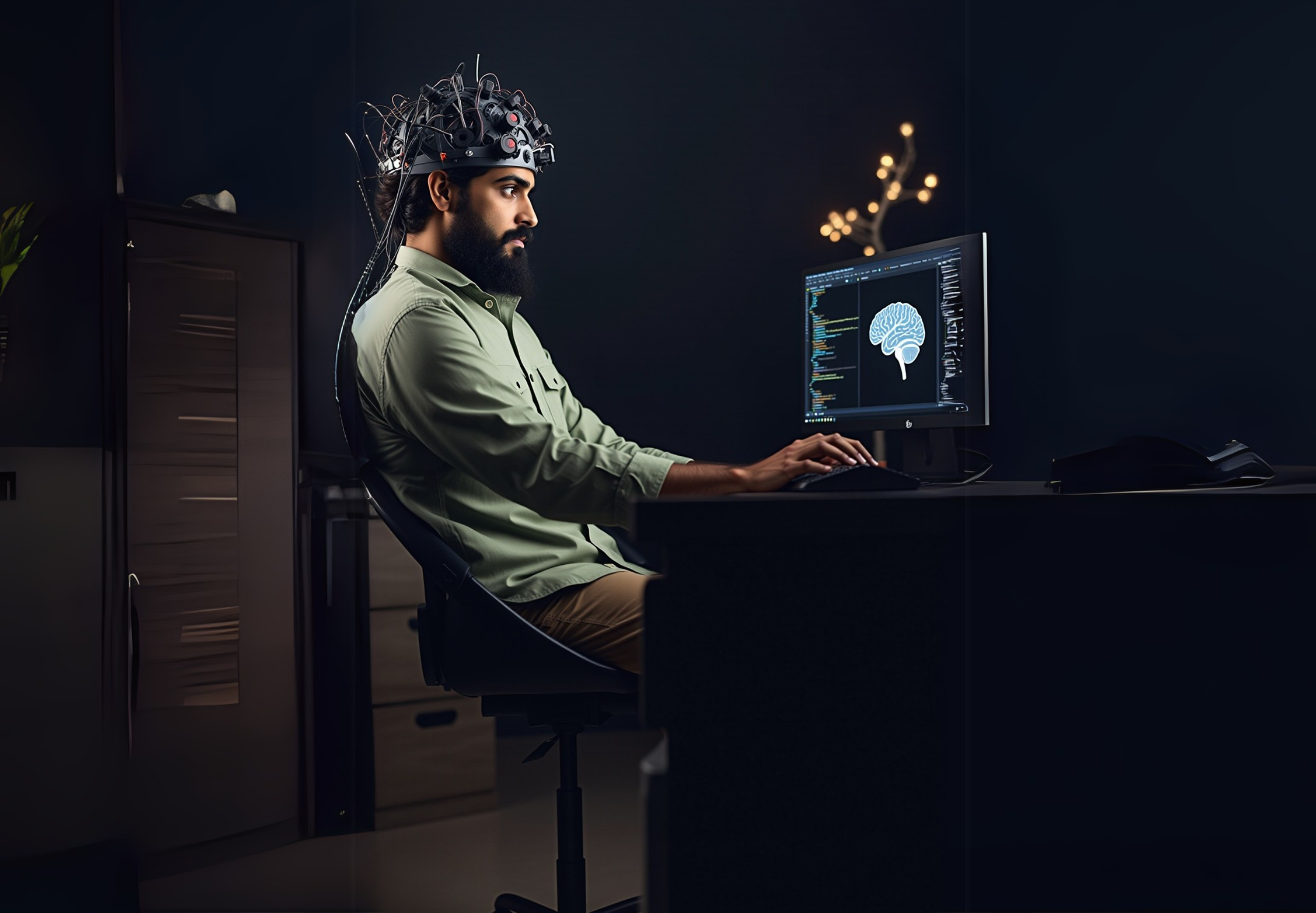
Brainwaves are measured using an EEG (electroencephalogram), a device that records electrical signals from the scalp. During neurofeedback therapy, sensors placed gently on your scalp detect your brainwave patterns and send the information to a computer, which then visually displays these waves in real-time. You can get this kind of therapy performed by the Mind Brian Institute which is located in New Delhi, India.
How Neurofeedback Works
Neurofeedback operates through a simple yet profound principle called operant conditioning, which involves rewarding desired behaviors to encourage repetition. When your brain produces healthier, more balanced brainwave patterns, you receive instant feedback—often visual or auditory signals—as a reward.
Over time, your brain learns to replicate these healthier patterns naturally, without effort. This process leads to lasting improvements in brain function, emotional regulation, and overall mental health.
Brainwave Patterns and Mental Health
Mental health conditions often correlate with imbalances or abnormalities in brainwave patterns. For example:
- Anxiety typically involves excessive Beta wave activity, particularly in high Beta (20-30 Hz), associated with heightened alertness and stress.
- Depression often corresponds with reduced Alpha activity, signaling difficulty in achieving calmness and relaxation.
- ADHD usually shows increased Theta waves and decreased Beta waves, indicating difficulty in maintaining attention and focus.
Treating Anxiety with Neurofeedback
Anxiety is one of the most common mental health challenges effectively addressed by neurofeedback. Individuals experiencing anxiety often exhibit overly active Beta waves, especially in the higher frequencies, which correlate with worry, restlessness, and racing thoughts.
During neurofeedback sessions for anxiety, the therapy targets reducing this excessive Beta activity and enhancing calmer Alpha wave production. By training the brain to lower Beta waves and increase Alpha waves, individuals can achieve a calmer state of mind.
Example Scenario: Neurofeedback Session for Anxiety
Imagine Sarah, who struggles with anxiety and persistent worry. During her neurofeedback session, sensors are gently placed on her scalp, measuring her brainwaves. As her brainwaves appear on the screen, Sarah sees real-time feedback in the form of a calming video or soothing sound.
When Sarah’s brain naturally shifts towards calmer Alpha frequencies and reduces high Beta frequencies, the calming visuals continue, rewarding her brain. If her mind wanders and anxiety returns, the feedback gently changes, prompting her brain to return to a relaxed state.
Over multiple sessions, Sarah’s brain gradually learns to maintain these calmer states independently, significantly reducing her anxiety symptoms.
Science Supporting Neurofeedback
Numerous scientific studies back neurofeedback’s effectiveness. Research consistently demonstrates significant improvements in anxiety, ADHD, depression, PTSD, insomnia, and even migraines. Studies using EEG scans before and after neurofeedback therapy show lasting shifts towards healthier brainwave patterns.
For example, a study published in the Journal of Clinical Psychophysiology found that individuals treated with neurofeedback for anxiety experienced substantial reductions in symptoms, alongside measurable changes in brainwave activity reflecting reduced stress and improved relaxation.
Advantages of Neurofeedback
- Drug-free treatment: Neurofeedback doesn’t require medication, making it ideal for those who prefer natural approaches.
- Personalized: Each treatment session is tailored to the individual’s unique brainwave patterns.
- Non-invasive: The treatment is painless and safe, without side effects commonly associated with medications.
- Long-lasting results: By training your brain, neurofeedback fosters enduring improvements.
Who Can Benefit from Neurofeedback?
Neurofeedback can benefit almost anyone seeking improved mental clarity, emotional regulation, and mental health. It’s particularly effective for:
- Individuals struggling with anxiety or chronic stress.
- Children and adults diagnosed with ADHD.
- Those dealing with depression or mood disorders.
- Individuals suffering from insomnia or sleep disorders.
- People looking to optimize cognitive performance or enhance creativity and focus.
What to Expect During Neurofeedback Therapy
A typical neurofeedback session lasts about 30 to 45 minutes. The therapist attaches sensors to your scalp using a gentle, conductive paste. You’ll sit comfortably as your brainwaves are displayed on a screen, receiving immediate feedback through calming visuals or sounds.
Most individuals report neurofeedback as relaxing and enjoyable. While results vary, improvements in anxiety symptoms are usually noticeable within 10 to 20 sessions.
Potential Challenges
Although generally safe and effective, neurofeedback isn’t an instant fix. It requires consistency and patience, as changes in brainwave patterns and mental health happen gradually.
Some individuals may initially experience mild fatigue, temporary increases in anxiety, or emotional sensitivity. However, these effects typically diminish quickly as the brain adjusts to the new patterns.
Integrating Neurofeedback into Daily Life
For optimal outcomes, neurofeedback therapy can be combined with lifestyle adjustments, including:
- Regular physical exercise.
- Mindfulness meditation practices.
- Adequate sleep hygiene.
- Balanced nutrition.
Integrating these healthy habits complements neurofeedback, fostering an environment where the brain can sustain positive changes long-term.
Conclusion: Empowering Your Brain for Better Health
Neurofeedback offers a fascinating glimpse into our brain’s ability to learn and adapt. By understanding and reshaping brainwave patterns, we can directly influence our emotional health, mental clarity, and overall quality of life.
As neuroscience advances, neurofeedback continues to establish itself as a powerful, evidence-based approach, providing hope and tangible benefits for those facing anxiety, depression, ADHD, and many other conditions.
By decoding the language of your brainwaves, neurofeedback empowers you to take charge of your mental health naturally, safely, and effectively.
*
To learn more about neurofeedback and its process, you may visit the Mind Brain Institute in New Delhi, India, or follow us on Instagram and YouTube.