- Posted By Dr. Anuranjan Bist
- Comments 0
Table of Contents
In the past few years, Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) Therapy has come forward as a promising technique in psychology, personal wellness, and neuroscience. From increasing concentration and memory to minimizing the depression system and chronic pain, tDCS benefits have attracted researchers and clinicians. But what is tDCS, and how does it work, and is it safe for applications?
In this blog, we’ll explore tDCS from the ground up, explaining the science, showcasing where it’s used, and clarifying safety concerns, with helpful diagrams along the way.
What is tDCS? The Science Explained
Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation is a brain stimulation method that doesn’t require any kind of invasion into the skin or the use of anesthesia. It uses low levels of constant direct current delivered through electrodes placed on the scalp. The objective of the technique is to modulate the activity of the brain by making neurons more or less likely to fire.
A typical tDCS therapy setup includes:
- Two electrodes: anodal (+) and cathodal (−)
- A low-voltage power source
- Conductive gel or saline-soaked sponges
With the current flowing through electrodes, it subtly alters the membrane potential of neurons in the targeted brain area. Stimulation due to anode increases excitability, promoting neuron firing, while cathodal stimulation can inhibit neural activity.
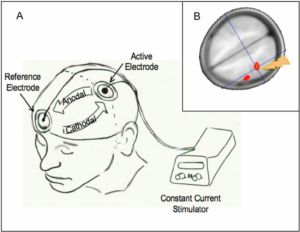
This method enables both clinicians and users to target specific brain regions, like the prefrontal cortex, to influence mood or the motor cortex to support movement recovery.
How Does tDCS Work?
Understanding Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation begins with the concept of neuroplasticity, the remarkable capacity of the brain to recognize its structure and functions based on experiences and stimuli. By making a slight alteration in resting membrane potential in neurons, tDCS neither compels them to fire but prepares them to be more or less likely to fire when involved in simultaneous activity.
Here’s a simple breakdown:
- Electrode placement determines the brain region to be targeted.
- Direct current flows between electrodes, influencing neurons below.
- Over time and repeated sessions, the brain adapts, enhancing learning or recovery.
Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation is usually combined with other activities, such as cognitive functions, physical therapy, or learning, to enhance effects. That’s because the effect is best when the brain is already engaged in the desired manner. This synergy is one of the most promising aspects of tDCS benefits.
Real-World Applications & Usage Contexts
Medical Applications
tDCS benefits and techniques have been researched thoroughly for its possible therapeutic potential in various conditions:
- Depression and anxiety: Stimulation of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex has been promising for reducing mood disorders.
- Chronic pain: tDCS therapy has been found to decrease neuropathic and fibromyalgia-type pain.
- Stroke rehabilitation: Enhancing motor cortex excitability supports motor recovery.
- Addiction and cravings: tDCS may reduce urges for substances like nicotine or alcohol.
Cognitive Enhancement
Beyond therapy, tDCS benefits extend into mental performance enhancement:
- Memory improvement
- Faster learning
- Improved attention and problem-solving
Students, researchers, and professionals have experimented with Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) to gain a cognitive edge, though results vary based on timing, electrode placement, and individual neurobiology.
Performance and Wellness
In sports and military settings, tDCS therapy is being tested for:
- Improved reaction time
- Enhanced motor learning
- Better stress management under pressure
Table: Common Applications of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation
Category | Use Case | Brain Area Targeted |
Medical | Depression, pain relief | Prefrontal, motor cortex |
Cognitive | Memory, focus | Prefrontal cortex |
Rehabilitation | Stroke, motor recovery | Primary motor cortex |
Wellness | Mood, relaxation, motivation | Frontal lobe, limbic areas |
Safety & Side Effects: What You Should Know
As fascinating as it sounds, Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) is very simple and, with responsible usage, safe for most individuals. That being said, it’s not completely risk-free, particularly in unsupervised or unregulated environments.
Common Side Effects of tDCS Therapy
- Mild tingling or itching under the electrodes
- Slight headache or fatigue
- Skin redness
- Dizziness in rare cases
These effects usually resolve quickly and are often related to incorrect electrode placement or excessive current levels.
Who Should Avoid tDCS Therapy?
- People with epilepsy
- Individuals with metal implants and pacemakers
- Pregnant individuals
- Children (unless under clinical supervision)
Safety Guidelines
- Always use medical-grade or approved consumer devices
- Follow protocols for electrode placement and duration
- Consult a professional if using it for therapeutic purposes
The U.S. FDA currently classifies tDCS devices for personal use as wellness products, though clinical use requires more rigorous approval.
Emerging Research and the Future of tDCS Therapy
As interest grows, so does the research. Current studies are exploring tDCS benefits in areas such as:
- ADHD and attention modulation
- PTSD treatment
- Neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s
- Language recovery after brain injuries
Technology is also evolving. App-integrated devices, AI-augmented stimulation mapping, and multi-channel tDCS systems are being designed to enhance treatments with personalization and efficacy.
But the scientific world is still wary. While initial findings are encouraging, larger, longer-term trials must be done to confirm tDCS therapy for some applications.
Conclusion: Is tDCS Therapy Worth a Try?
Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation is a thrilling frontier in brain science, one where simplicity meets great promise. It ranges from clinical treatment to individual productivity, where tDCS benefits are discovered in various fields. But it’s no magic switch for enhancing the brain and must be considered carefully.
If you’re considering trying tDCS therapy:
- Understand your goals (therapy vs. enhancement)
- Use only certified devices
- Follow recommended safety protocols
- Think about talking to someone like a neurologist or mental health practitioner
As studies continue to progress, tDCS therapy has the potential to be a less expensive and more consistent method of unlocking the brain’s full capacity, safely and effectively.
Key Takeaways:
- tDCS therapy is a pain-free way of brain stimulation with the use of low-intensity electrical currents.
- It affects neuroplasticity to enhance mood, cognition, and healing.
- tDCS advantages are in therapy, learning, wellness, and rehabilitation.
- It is safe in general, but must be used responsibly.
- Future research may further validate its widespread use.
Want to know more? Contact us or explore your key to better mental health with our services at Mind Brain Institute.